Map Catalog-Danielle Schwartz
Sunday, November 20, 2011
Bivariate Choropleth Map
A bivariate choropleth map is a type of choropleth map that compares two variables of data on one map. The two variables can be distinguished using different colors or symbols. By comparing variables together, you can analyze their correlation. The difference between a bivarate map and a bivaraite choropleth map is the choropleth map cannot display data using lines or points. The bivariate choropleth map shown compares the population of Ohio in 1997 with median house values.
http://proceedings.esri.com/library/userconf/proc99/proceed/papers/pap171/p171.htm
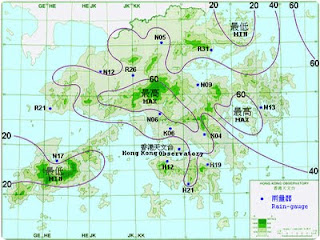
Black and White Aerial Photograph
A black and white aerial photograph is a type of aerial photograph used in remote sensing. Black and white photographs show the same wavelength as the human eye. Structures and features that have a similar shade of gray may be hard to distinguish in a black and white aerial photograph compared to an IR aerial photographs. The example black and white aerial photograph shown above is a picture of New York City. The similar shades of gray in objects closer to the ground are difficult to distinguish.
http://research.shu.ac.uk/lab4living/about/people/professor-paul-chamberlain
Enhanced Thermatic Mapper
The Enhanced Thematic Mapper is found on the Landsat 7 satellite. It is a type of remote sensing that falls under the category of multispectral imagery. The Enhanced Thematic Mapper records seven bands that are divided by wavelength. The images taken are useful when comparing before and after images. The area of the real world image can be determined by counting the number of pixels. The example Enhanced Thematic Mapper illustration shown above, exhibits the before and after photographs of Japan after an earthquake and tsunami on March 11, 2011.
http://www.earthzine.org/2011/03/23/earth-observation-resources-on-the-tsunami/
Parallel Coordinate Map
A parallel coordinate map is a way to show multidimensional problems. The map appears confusing, but is useful when identifying outliers. Each variable being compared is found on the x- axis. When the lines are close together, it is high correlation. The example parallel coordinate map above shows a map for nine selected genes labeled across the x-axis.
http://vis.lbl.gov/Vignettes/Drosophila/index.html
Unstandardized Choropleth Map
An unstandardized choropleth map is a type of choropleth map that has not been aerially averaged. Instead of using numerical values, ranges, or ratios, different shades of colored are used to differences in data. The example choropleth map shows the different ethnic groups across Afghanistan.
http://www.mazardevelopmentfund.org.au/afghanistan.htm
Nominal Area Choropleth Map
A nominal area choropleth map is a type of choropleth map that classifies data into groups in a qualitative manner. Nominal area choropleth maps have no implicit ordering. The example nominal area choropleth map displays the minority group with the highest percent of state population and is presented in a qualitative manner. The map shows that in the east the African American minority groups have the highest population, and in the west, the Hispanic minority groups have the highest population.
https://courseware.e-education.psu.edu/courses/geog482/policies.shtml
Triangular Plot
A triangular plot is used to graph the ratios of three separate variables in an equilateral triangle. The plot is known to be convenient because three variables can be graphed in a two dimensional plot. Triangular plots are most often used in geologic studies. The example triangular plot shows the chemical analysis of igneous rock. The three variables graphed, tholeiitic, mantle magma, and calc-alkaline, are easily identifiable.
http://www.lithoprobe.ca/media/slideset/slides/tools20.asp.
Standardized Choropleth
A standardized choropleth map is a type of choropleth map where the area is standardized to allow for easy comparison across different areas. Standardization is useful because the different sizes of the area mapped may alter the impression given off. Some examples of standardization include land area, percents, rates, ratios, per capita, or any per capita variable. The picture above in an example standardized choropleth map of North Carolina. The per pupil expenditure for public education in North Carolina is divided into ranges distinguished by different shades of the color blue.
http://personal.uncc.edu/lagaro/cwg/color/Choro5-SingleHueGood.gif
Soil Map
A soil map provides information from a soil survey about the type of soil in a certain area. The soil map is useful for land planning for vegetation, environmental protection, highways, roads, and even building proposals. The picture above is a soil map for the state of Texas. It is interesting to see the vast amount of different soils that can be found in one state.
http://www.brc.tamus.edu/news/last-acre
Infrared Aerial Photograph
An infrared aerial photo is a type of aerial photograph that uses a specific spectrum of light called electromagnetic radiation. Infrared aerial photographs are useful in monitoring changes and damages in the environment or to buildings and structures. They also can be used to determine the type and health of vegetation in a certain area. The picture above is an example of an infrared aerial photograph of a forest in Harford County, Maryland. The photograph shows the forest has been damaged by Gypsy Moths.
http://www.visualphotos.com/image/1x3740445/ir_image_of_moth-damaged_forest_infrared_aerial_of
Cartogram
A Cartogram is a not a true map. Cartograms display statistical data through the use of line, dots, or shaded areas. Cartograms can resemble real maps or not look like a map at all. The two main types of cartograms are area and distance. Area cartograms commonly show populations while distance maps commonly show time travel and direction. Cartograms can also be broken down into the categories of contiguous, non-contiguous, dorling, and pseudo. The picture above is an example cartogram from the 2008 election. The map resembles the United States, but it’s obvious that the map has been deformed. It is still apparent that most of the country voted democratic.
http://www-personal.umich.edu/~mejn/election/2008/
Statistical Map
A Statistical map is a type of map that shows results of a statistical test on a map. Statistical maps are used to display a certain variable over a geographical area or time. The two maps pictured above show the results of a statistical test on the amount of people who have Internet, Bitnet, email only, and no connectivity across the world in the year of 1991 and 1997.
http://personalpages.manchester.ac.uk/staff/m.dodge/cybergeography/atlas/census.html
Light Detection and Ranging
Light Detection and Ranging also known as LIDAR is a type of active remote sensing. The sensor is attached to an airplane along with a GPS and an inertial navigation system. LIDAR uses pulses of light to show the terrain. The elevation of terrain can be measured by recording the differences in time the laser takes to reach the point being measured. The pictures above show the differences in the LIDAR of the world trade center before and after the September 11th attacks.
http://www.loc.gov/exhibits/911/911-maps.html
Public Land Survey System
A Public Land Survey System is used to subdivide the land. A PLSS differs from the average coordinate system because it is more descriptive and relies less on absolute measurements of location. In the United States the PLSS is regulated by the U.S Department of the Interior, Bureau of Land Management. The PLSS is used to divide land that is owned by the Federal government. The picture above shows a PLSS of Alaska. The map shows map shows Alaska is divided into five sections.
http://www.ak.nrcs.usda.gov/technical/plss.html
Range Graded Proportional Circle Map
Range graded proportional circle map is another type of proportional circle map that displays data using circles to represent data instead of dots. The size of the circle relates to the measured variable and not the area it is covering. There are only a set number of circle sizes that are used in each map. The amount is designed based on information being displayed. The map above is an example of a range graded proportional circle map. Using four different sized dots, the amount of inhabitants of the communes in the region of Zurich can be displayed for easy analysis.
http://www.e-cartouche.ch/content_reg/cartouche/cartdesign/en/html/ThemMaps_ThemData.html
Continuously Variable Proportional Circle Map
A continuously variable proportional circle map is a type of proportional circle map that displays data using circles to represent data instead of dots. The size of the circle relates to the measured variable and not the area it is covering. There is not a specific amount of circles used, and the size can vary. The circles are divided into pie charts. This allows other information to be displayed. The continuously variable proportional circle map above is from 1858. The map displays the differences in amount and type of meat that was sent to Paris butcheries from different regions of France.
https://www.e-education.psu.edu/geog486/book/export/html/1796
Correlation Matrix
A correlation matrix is a type of chart that is used in statistical analysis. A correlation is the relationship between two separate variables. A single number calculated by a serious of steps using the correlation formula represents the correlation. The actual correlation is represented by the letter r. If the answer to r is zero, the null hypothesis in the statistical test is the conclusion. If the answer is greater than or less than r, the alternative hypothesis is the conclusion. The chart pictured above in a correlation matrix of for phage T7. The diagonal of the correlation matrix is always one because the one represents the correlation between each variable and itself.
http://yin.che.wisc.edu/images.htm
Digital Line Graph
A DLG is derived from USGS maps or USGS map-related sources. DLGs can be made on three different scales: large scale, intermediate scale, and small scale. A DLG is a type of digital vector data. The data displayed can come from a wide range of variables including, but not limited to, topography, hydrography, boundaries, roads, and utility lines. The data is presented in vectors and stored as arcs, points, and polygons. The picture above is an example DLG of Beaufort, South Carolina.
http://www.dnr.sc.gov/GIS/descdlg.html
Digital Raster Graphic
A definition of a DRG is a scanned image of a U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) standard series topographic map. DRGS are most useful as backdrops where other digital data is superimposed. The san of a DRG is 250 pixels per inch resolution. The picture above is a DRG of Bushkill, Pennsylvania.
https://www.e-education.psu.edu/natureofgeoinfo/c6_p6.html
Digital Orthographic Quarter- Quad
A DOQQ is a type of geographic information system that combines an aerial photograph with the geometric qualities of a map. The aerial photograph of a DOQQ is distorted due to terrain relief and camera tilts. Due to this, the photograph has been georeferenced and orthocrectified. This helps remove the distortion of the areal photographs. By limiting distortion, accurate measures of distance, angels, area, positions can be determined. The picture above shows a DOQQ of Washington DC with a 1m resolution.
http://seamless.usgs.gov/products/1doqq.php
Sunday, November 13, 2011
Univariate Chloropleth Map
A univariate chloropleth map is a type of map that only portrays one variable. The different findings from the data are displayed using different colors. Univariate chloropleth maps are the most common type of chloropleth map and the easiest to interpret. The picture above shows a univariate chloropleth map of the health of the states population. The darker the color red,the healthier the states. The white states are the unhealthiest states.
http://depositphotos.com/4439591/stock-photo-Healthiest-vs-Unhealthiest---United-States-Map.html
Classed Chloropleth Maps
In a classed chloropleth map the variables of data are combined into groups. These groups are then portrayed in intervals. A classed chloropleth map is best designed using four to seven intervals. The intervals can be divided up using the techniques of equal steps, quantiles, natural breaks, or minimum variance. The picture above shows a classed chloropleth map of the United States water usage. The different shades of blue represent the five different intervals of range of use. This classed chloropleth map is most likely an equal step classification, due to the fact that the total range is divided into categories which were most likely designed by the map designer. The drawbacks in the map can be seen with the amount of states in each category. The top category only has three states where the 2,000 to 5,000 million gallons per day category contains 19 states.
http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/wateruse2000.html
Cadastral Map
A cadastral map is type of map that identifies boundaries of land ownership. These maps are available for public use, but are maintained by the government. Information found on this type of map may include: who owns the land, zoning, tax rates, and certain items found on the property. The picture above shows an example cadastral map of what looks like to be a neighborhood. The separation of lots and their individual size is easily identifiable.
http://www.fig.net/cadastraltemplate/fielddata/d2.htm
Monday, November 7, 2011
Line Graph
A line graph is a type of geovisualization. The graph is used to compare an independent variable verses a dependent variable. The dependent variable is usually time. Line graphs can consist of one or more lines. Data from an experiment is plotted on the graph, and a line is used to connect the data to show a trend. A line graph is an extension of a scatter plot and has many similar characteristics. The picture above shows a line graph of the amount of people who switch from AT&T to MCI over a period of time. The trend shows a positive correlation between time and number of people who switched companies.
http://mste.illinois.edu/courses/ci330ms/youtsey/lineinfo.html
Pie Chart
A part chart is a type of geovisualization. It is a chart that is used to compare different dependent variables from a common independent variable. The graph is in a circular pie shape and is usually multiple colors to help for easy analysis. Pie charts can be used to measure many things including both quantitative and qualitative data. The pie chart above shows the results of the question: what is your favorite movie? The chart shows how many students were asked and how many chose each different category. The percentages were also calculated.
http://www.mathsisfun.com/data/pie-charts.html
Isohyet
An isohyet is a type of contour map that measures the equal amount of rainfall in a given area during a certain time period. Due to the fact that the amount of rainfall can vary from year to year, theses maps can help analyze climate variability. The picture above is an isohyet from Asia. Areas that received the same amount of rainfall are connected by contour lines. According to the map, most of the area received 40 (can’t tell units) of rain.
http://www.einfopedia.com/tag/what-is-isohyet
Sunday, October 30, 2011
Bathymetric Map
A Bathymetric map is a type of contour map that measures sea floor elevation. It is measured and designed in the same way as a topographic map. The depth of the ocean floor is measured through the use of depth sounding. The picture above shows a bathymetric map of the world’s oceans. The different depths are easily seen through use of a key: the deeper the ocean, the deeper the color blue. Bathymetric maps are useful for marine navigation and studies.
http://maps.grida.no/go/graphic/world-ocean-bathymetric-map
Isopach
An isopach map is a type of contour map that measures equal rock or sediment thickness. Isopachs disregard geological reasons for thickening and thinning of different formations. Isopachs can be useful for many reasons such as estimating the volumes of volcanic ashes. The isopach pictured above uses contour lines and colors to show the difference in sediment thickness of the Rio Blanco Tephra Deposit.
http://www.geo.utexas.edu/faculty/barker/kempter/rbtephra.html
Isotach
An isotach is a type of contour map that is used in meteorology to measure equal wind speeds. Through the use of contour lines and different colors, the different speeds and forces can be shown. This type of map is used to locate the jet stream and jet streaks. The picture above is an isotach for the United States. Using a key, the speed and force of the wind for different states can be determined by comparing the different colors and symbols.
http://www.erh.noaa.gov/gsp/localdat/cases/2008/IdesOfMarchSupercells/IdesOfMarch2008.html
Sunday, October 23, 2011
Isobar

An isobar is a commonly used chart in meteorology that shows equal barometric pressure. There are four rules when drawing isobars. 1. Isobars can never cross or touch. 2. Isobar lines can only pass through pressures of 1000 +/- 4. 3. The atmospheric pressure is given in millibars. 4. Different pressures due to elevation are ignored. The isobar map pictured above exhibits the different levels for pressure during a low-pressure system near West Virginia and Ohio.
http://rst.gsfc.nasa.gov/Sect14/Sect14_1c.html
Topographic Map
A topographic map is similar to a planimteric map, however, elevation and depth are included. Contour lines and different colors are used to distinguish between the topography of different areas. The detail allows for easy analysis of the land being mapped. Topographic maps are most commonly used as GPS devices. Topographic maps are sometimes referred to as contour maps. The picture above is a historic topographic map. The contour lines and different colors seen in the map distinguish the different elevations of the location presented.
http://www.gelib.com/historic-topographic-maps.htm
Planimetric Map
A Planimetric map, sometimes called a line map or street map, is a map that is used to show only the horizontal position for the location shown. Elevation and depth are not included on the map. Planimetric maps are used for special reasons and can be designed in different ways. Planimetric maps can show transportation routes, water bodies, valleys and mountains minus their elevation or depth. The Planimetric map shown above displays the outline of Buckthorn Drive. The road, homes, and trees are shown without elevation or height.
http://www.webs1.uidaho.edu/niatt_labmanual/Chapters/roadwaydesign/theoryandconcepts/SurveysAndMaps.htm
Sunday, October 16, 2011
Similarity Matrix
A similarity matrix is a type of matrix that shows the similarities between two variables of data. A stronger similarity implies a greater value of measure. The picture exhibits a similarity matrix from the SRI Malware Cluster Laboratory. The level of similarity is shown using colors. The more similar results are identified by the highest number which in this example is 1.0. The number one is pictured on the graph using the color red. The areas of least similarity are colored blue.
http://cgi.mtc.sri.com/Cluster-Lab/
Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
A DEM is a model that is used to represent the height of earth surface for the given area. Most DEMs are completed by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). DEM uses a fixed grid interval that is always referenced to some geographical coordinate system. The DEM is a generic form of the DSM and DTM. The picture above shows a DEM for the state of California. It is interesting to note the changes in elevations throughout the state of California due to its vast size.
http://mapsof.net/map/digital-elevation-map-california
Bilateral Graph
A bilateral graph portrays the comparison of two related variables. The graph can display positive and negative data. The chart can be displayed as a curve, line, or bar graph. The bilateral bar graph picture above shows the Profit- and Dividend Status of 348 Corporations in the United States for the period from 1929 to 1935.
http://www.scribd.com/doc/53502496/5/BILATERAL-BAR-CHARTS
Sunday, October 9, 2011
Scatterplot
A scatter plot is a plot that shows the relationship between a dependent and independent variable on a Cartesian coordinate. This type of plot is used commonly in experimental data collection with many trials. After all the data has been collected, a scatter plot can be formed. A line of best fit is then drawn to help determine the correlation and factors such as acceleration of a certain object. The example scatter plot comes from my biochemistry lab. The experiment was on enzyme kinetics. A scatter plot was used to display the relationship between substrate concentration verses the initial velocity. A line of best fit was determined. The numbers from the best fit line were used to calculate the maximum rate of the catalyzed reaction and the KM.
Box Plot
A box plot or box and whisker plot is a graph that is used to display statistical data. The box plot consists of five parts. The beginning of the plot starts with the minimum value of the data. The second point, the lower quartile, signals the formation of the box. The third point signals the median value of the data. The fourth point, the upper quartile, signals the end of the box. The fifth point signals the maximum point for the set of data. The box plot can be used to analyze data. It is easy to show if the data is skewed, and it is easy to determine outliers. The example picture uses multiple box plots to show the relationship between the day of the week and the amount of times a certain website was hit. It can be determined that Tuesday had the most hits, and Monday had the widest range for amount of hits. It can also be determined that this website may be used mostly by businesses because Saturday had the least amount of hits and the most outliers.
Ex. --> to show where points located
http://support.sas.com/rnd/app/da/new/daunivariate.html
http://ellerbruch.nmu.edu/cs255/jnord/boxplot.html
Thematic Map
A thematic map is a map that is used to show the relationship of a variable over a certain area. The five types of thematic maps are the choropleth map, graduated symbols, contour map, dot map, and dasymetric mapping. Choropleth maps show quantitative data using different colors. A gradated symbol map uses symbols to represent data. A contour map uses isolines. A dot map uses dots to show a spatial pattern. A dasytmetric map is similar to the choropleth but uses extra statistics. The example thematic map shows the results of the 2000 presidential election. The map would be classified as a type of dasymetric map because like a choropleth map, it uses colors. It also uses statistical data, or Electoral College votes.
http://kc-johnson.com/week-of-april-27/
Sunday, October 2, 2011
Wind Rose
A wind rose map is a map used by meteorologist to help determine the wind speed and direction. The map is measured using concentric circles. Each circle represents a different speed or frequency of the wind. The direction of the spoke shows the direction of the wind. The map shows data on the average wind speed and direction for a particular length of time. A key is used with different colors, much like a Doppler radar, to show the differences in wind strength. The example wind rose pictured above shows the wind direction and speed for Hurricane Frances and Jeanne in August of 2004.
http://www.plantmanagementnetwork.org/pub/php/research/2006/canker/
Cartographic Animation
Cartographic animation, also known as animated mapping, is a map that allows the viewer to see the change of what is being mapped over a variable. The types of variables used in this type of mapping can be divided into temporal and non-temporal. A temporal map measures a change over time. These maps are most commonly used in weather forecasting. Not only do these maps show the change in weather over time, but they also show the direction of the weather system being tracked. A non-temporal map can have many different types of variables. An example of a non-temporal map is a fly over. A fly over involves a change in location being presented through a series of maps in quick succession. The picture above is an example of a temporal cartographic animation of hurricane Ivan. The cartographic animation showed the path of the hurricane over time.
http://hurricanehistory.org/resources/Hurricane-Ivan.html
Stem and Leaf Plot
A stem and leaf plot is a type of plot that helps organize data. It is comprised of two sections, the stem and the leaf. The steam column holds all numbers except the number in the ones place. The leaf column holds the number in the ones place. For example, if you had the number 927 the nine and two would be in the stem column and the seven would be in the leaf column. By organizing data into stem and leaf plots, identification of trends throughout the data can be easily seen. It also makes it simple to find the median and mode of the number set. The example stem and leaf plot pictured above shows a range of temperatures recorded over a period of time.
http://emed.nucenter.org/groups/dataprobability/blog/
Sunday, September 25, 2011
Flow Map
A flow map is a type of map that shows the movement of something from one place to another. These maps are used on a day-to-day basis to exhibit many different types of information. For example, many airlines use a flow map to show the different locations to which their company flies. The more lines pointing to a location, the more flights that location receives. Flow maps can basically be used to depict anything that moves from one location to another. The picture above is an example of a flow map that displays traffic. The lines near the big cities become darker showing the increased traffic in those areas.
http://mundi.net/maps/maps_014/
Histograms
Histograms are a type of map that is used to organize data. The data is organized into a bar graph to allow easy analysis. There are many different options for the variables on a histogram, but the data is usually numerical. The horizontal axis usually contains the independent variable and the vertical axis usually contains the dependent variable. The example histogram showed uses the variables of score on a final exam verses number of students who received this score.
http://searchsoftwarequality.techtarget.com/definition/histogram
Mental Map
A mental map is a map that is made by an individual based on his or her own thoughts. Most mental maps, when drawn, show an emphasis on certain landmarks or areas that are important to the individual who designed the map. These maps can be useful when trying to describe locations or directions to a certain area. In the picture of the mental map, locations such as school, the designer’s home, and church are emphasized. This implies that these locations are important to the designer.
http://mentalcharlois.wordpress.com/tag/mental-mapping/
Sunday, September 18, 2011
Climograph
A climograph is a graph that is used to show the range of monthly temperature and precipitation for a certain location. Travelers or people looking for information about a specific location most frequently use these maps. The map allows the viewer to develop an idea of what the weather is like for a certain period. Awareness of what weather to expect can help with travel plans or even moving plans. I am in the process of applying to dental school. I have never been to Phoenix, Arizona, but I did apply to two schools located there. I had always been told that the weather is quite moderate and there is not a lot of rain. The maps, such as the one shown above, would illustrate the weather that I can expect during the months I would be there.
http://www.usclimatedata.com/climate.php?location=USAZ0166
Population Profile
A population profile is a type of map that is used to show the demographics of a population. The map shows an analysis of the number of people in a location as a function of their age. These maps can then be used for statistical conclusions for the locations being measured. The picture above shows a population profile of Ketton. As one can see from the map, the largest part of the population in Ketton consists of people between the ages of 34-54 followed by the second highest being people between the ages of 55-64. If one were to look at this population profile, conclusions could then be made for statistical data. The map could also be used to help with attraction building. Due to the fact that the population can be classified as middle age adults, attractions should be placed in Ketton that attract an older crowd rather than, for example, a bar that attracts young adults who make up the smallest part of the population.
http://www.rutnet.co.uk/pp/gold/viewGold.asp?IDType=Page&ID=13868
Propagana Map
A propaganda map is a map that is used to portray or convince people of an idea. Propaganda maps can be considered to be a type of arbitrary cartography because one can design the map to specifically show a particular opinion. Propaganda maps have been used throughout history and have proven to be very successful. The map shown below is a propaganda map of Florida. The map portrays the positive attractions of Florida, such as the beaches, certain animals such as dolphins and pelicans, and even a space ship to show where Kennedy Space Center is located. If someone who has never been to Florida and knew nothing about the state were to see this map, they would believe that Florida is the ideal place to travel. Notice the designer’s propaganda map is trying to portray Florida in a positive manner, and has purposely failed to display thunderstorms and hurricanes, even though these are a common occurrences.
http://www.rainbowcountrytravel.com/florida-fun-spots/
Monday, September 5, 2011
Hypsometric Map
Hypsometric maps are used to show the topography and elevation of the land being displayed. The different types of topography and elevation are represented by different colors and shading. The colors green, beige, yellow, red, and white are most commonly used. The color green represents lower elevations while beige and yellow represent a higher elevation. This type of map is also used to show differences in ocean depth. The darker the color blue the deeper the ocean. The example hypsometric map shows the different levels of elevation in Spain.
http://maps.aridocean.com/
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)