Sunday, November 20, 2011
Bivariate Choropleth Map
A bivariate choropleth map is a type of choropleth map that compares two variables of data on one map. The two variables can be distinguished using different colors or symbols. By comparing variables together, you can analyze their correlation. The difference between a bivarate map and a bivaraite choropleth map is the choropleth map cannot display data using lines or points. The bivariate choropleth map shown compares the population of Ohio in 1997 with median house values.
http://proceedings.esri.com/library/userconf/proc99/proceed/papers/pap171/p171.htm
Black and White Aerial Photograph
A black and white aerial photograph is a type of aerial photograph used in remote sensing. Black and white photographs show the same wavelength as the human eye. Structures and features that have a similar shade of gray may be hard to distinguish in a black and white aerial photograph compared to an IR aerial photographs. The example black and white aerial photograph shown above is a picture of New York City. The similar shades of gray in objects closer to the ground are difficult to distinguish.
http://research.shu.ac.uk/lab4living/about/people/professor-paul-chamberlain
Enhanced Thermatic Mapper
The Enhanced Thematic Mapper is found on the Landsat 7 satellite. It is a type of remote sensing that falls under the category of multispectral imagery. The Enhanced Thematic Mapper records seven bands that are divided by wavelength. The images taken are useful when comparing before and after images. The area of the real world image can be determined by counting the number of pixels. The example Enhanced Thematic Mapper illustration shown above, exhibits the before and after photographs of Japan after an earthquake and tsunami on March 11, 2011.
http://www.earthzine.org/2011/03/23/earth-observation-resources-on-the-tsunami/
Parallel Coordinate Map
A parallel coordinate map is a way to show multidimensional problems. The map appears confusing, but is useful when identifying outliers. Each variable being compared is found on the x- axis. When the lines are close together, it is high correlation. The example parallel coordinate map above shows a map for nine selected genes labeled across the x-axis.
http://vis.lbl.gov/Vignettes/Drosophila/index.html
Unstandardized Choropleth Map
An unstandardized choropleth map is a type of choropleth map that has not been aerially averaged. Instead of using numerical values, ranges, or ratios, different shades of colored are used to differences in data. The example choropleth map shows the different ethnic groups across Afghanistan.
http://www.mazardevelopmentfund.org.au/afghanistan.htm
Nominal Area Choropleth Map
A nominal area choropleth map is a type of choropleth map that classifies data into groups in a qualitative manner. Nominal area choropleth maps have no implicit ordering. The example nominal area choropleth map displays the minority group with the highest percent of state population and is presented in a qualitative manner. The map shows that in the east the African American minority groups have the highest population, and in the west, the Hispanic minority groups have the highest population.
https://courseware.e-education.psu.edu/courses/geog482/policies.shtml
Triangular Plot
A triangular plot is used to graph the ratios of three separate variables in an equilateral triangle. The plot is known to be convenient because three variables can be graphed in a two dimensional plot. Triangular plots are most often used in geologic studies. The example triangular plot shows the chemical analysis of igneous rock. The three variables graphed, tholeiitic, mantle magma, and calc-alkaline, are easily identifiable.
http://www.lithoprobe.ca/media/slideset/slides/tools20.asp.
Standardized Choropleth
A standardized choropleth map is a type of choropleth map where the area is standardized to allow for easy comparison across different areas. Standardization is useful because the different sizes of the area mapped may alter the impression given off. Some examples of standardization include land area, percents, rates, ratios, per capita, or any per capita variable. The picture above in an example standardized choropleth map of North Carolina. The per pupil expenditure for public education in North Carolina is divided into ranges distinguished by different shades of the color blue.
http://personal.uncc.edu/lagaro/cwg/color/Choro5-SingleHueGood.gif
Soil Map
A soil map provides information from a soil survey about the type of soil in a certain area. The soil map is useful for land planning for vegetation, environmental protection, highways, roads, and even building proposals. The picture above is a soil map for the state of Texas. It is interesting to see the vast amount of different soils that can be found in one state.
http://www.brc.tamus.edu/news/last-acre
Infrared Aerial Photograph
An infrared aerial photo is a type of aerial photograph that uses a specific spectrum of light called electromagnetic radiation. Infrared aerial photographs are useful in monitoring changes and damages in the environment or to buildings and structures. They also can be used to determine the type and health of vegetation in a certain area. The picture above is an example of an infrared aerial photograph of a forest in Harford County, Maryland. The photograph shows the forest has been damaged by Gypsy Moths.
http://www.visualphotos.com/image/1x3740445/ir_image_of_moth-damaged_forest_infrared_aerial_of
Cartogram
A Cartogram is a not a true map. Cartograms display statistical data through the use of line, dots, or shaded areas. Cartograms can resemble real maps or not look like a map at all. The two main types of cartograms are area and distance. Area cartograms commonly show populations while distance maps commonly show time travel and direction. Cartograms can also be broken down into the categories of contiguous, non-contiguous, dorling, and pseudo. The picture above is an example cartogram from the 2008 election. The map resembles the United States, but it’s obvious that the map has been deformed. It is still apparent that most of the country voted democratic.
http://www-personal.umich.edu/~mejn/election/2008/
Statistical Map
A Statistical map is a type of map that shows results of a statistical test on a map. Statistical maps are used to display a certain variable over a geographical area or time. The two maps pictured above show the results of a statistical test on the amount of people who have Internet, Bitnet, email only, and no connectivity across the world in the year of 1991 and 1997.
http://personalpages.manchester.ac.uk/staff/m.dodge/cybergeography/atlas/census.html
Light Detection and Ranging
Light Detection and Ranging also known as LIDAR is a type of active remote sensing. The sensor is attached to an airplane along with a GPS and an inertial navigation system. LIDAR uses pulses of light to show the terrain. The elevation of terrain can be measured by recording the differences in time the laser takes to reach the point being measured. The pictures above show the differences in the LIDAR of the world trade center before and after the September 11th attacks.
http://www.loc.gov/exhibits/911/911-maps.html
Public Land Survey System
A Public Land Survey System is used to subdivide the land. A PLSS differs from the average coordinate system because it is more descriptive and relies less on absolute measurements of location. In the United States the PLSS is regulated by the U.S Department of the Interior, Bureau of Land Management. The PLSS is used to divide land that is owned by the Federal government. The picture above shows a PLSS of Alaska. The map shows map shows Alaska is divided into five sections.
http://www.ak.nrcs.usda.gov/technical/plss.html
Range Graded Proportional Circle Map
Range graded proportional circle map is another type of proportional circle map that displays data using circles to represent data instead of dots. The size of the circle relates to the measured variable and not the area it is covering. There are only a set number of circle sizes that are used in each map. The amount is designed based on information being displayed. The map above is an example of a range graded proportional circle map. Using four different sized dots, the amount of inhabitants of the communes in the region of Zurich can be displayed for easy analysis.
http://www.e-cartouche.ch/content_reg/cartouche/cartdesign/en/html/ThemMaps_ThemData.html
Continuously Variable Proportional Circle Map
A continuously variable proportional circle map is a type of proportional circle map that displays data using circles to represent data instead of dots. The size of the circle relates to the measured variable and not the area it is covering. There is not a specific amount of circles used, and the size can vary. The circles are divided into pie charts. This allows other information to be displayed. The continuously variable proportional circle map above is from 1858. The map displays the differences in amount and type of meat that was sent to Paris butcheries from different regions of France.
https://www.e-education.psu.edu/geog486/book/export/html/1796
Correlation Matrix
A correlation matrix is a type of chart that is used in statistical analysis. A correlation is the relationship between two separate variables. A single number calculated by a serious of steps using the correlation formula represents the correlation. The actual correlation is represented by the letter r. If the answer to r is zero, the null hypothesis in the statistical test is the conclusion. If the answer is greater than or less than r, the alternative hypothesis is the conclusion. The chart pictured above in a correlation matrix of for phage T7. The diagonal of the correlation matrix is always one because the one represents the correlation between each variable and itself.
http://yin.che.wisc.edu/images.htm
Digital Line Graph
A DLG is derived from USGS maps or USGS map-related sources. DLGs can be made on three different scales: large scale, intermediate scale, and small scale. A DLG is a type of digital vector data. The data displayed can come from a wide range of variables including, but not limited to, topography, hydrography, boundaries, roads, and utility lines. The data is presented in vectors and stored as arcs, points, and polygons. The picture above is an example DLG of Beaufort, South Carolina.
http://www.dnr.sc.gov/GIS/descdlg.html
Digital Raster Graphic
A definition of a DRG is a scanned image of a U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) standard series topographic map. DRGS are most useful as backdrops where other digital data is superimposed. The san of a DRG is 250 pixels per inch resolution. The picture above is a DRG of Bushkill, Pennsylvania.
https://www.e-education.psu.edu/natureofgeoinfo/c6_p6.html
Digital Orthographic Quarter- Quad
A DOQQ is a type of geographic information system that combines an aerial photograph with the geometric qualities of a map. The aerial photograph of a DOQQ is distorted due to terrain relief and camera tilts. Due to this, the photograph has been georeferenced and orthocrectified. This helps remove the distortion of the areal photographs. By limiting distortion, accurate measures of distance, angels, area, positions can be determined. The picture above shows a DOQQ of Washington DC with a 1m resolution.
http://seamless.usgs.gov/products/1doqq.php
Sunday, November 13, 2011
Univariate Chloropleth Map
A univariate chloropleth map is a type of map that only portrays one variable. The different findings from the data are displayed using different colors. Univariate chloropleth maps are the most common type of chloropleth map and the easiest to interpret. The picture above shows a univariate chloropleth map of the health of the states population. The darker the color red,the healthier the states. The white states are the unhealthiest states.
http://depositphotos.com/4439591/stock-photo-Healthiest-vs-Unhealthiest---United-States-Map.html
Classed Chloropleth Maps
In a classed chloropleth map the variables of data are combined into groups. These groups are then portrayed in intervals. A classed chloropleth map is best designed using four to seven intervals. The intervals can be divided up using the techniques of equal steps, quantiles, natural breaks, or minimum variance. The picture above shows a classed chloropleth map of the United States water usage. The different shades of blue represent the five different intervals of range of use. This classed chloropleth map is most likely an equal step classification, due to the fact that the total range is divided into categories which were most likely designed by the map designer. The drawbacks in the map can be seen with the amount of states in each category. The top category only has three states where the 2,000 to 5,000 million gallons per day category contains 19 states.
http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/wateruse2000.html
Cadastral Map
A cadastral map is type of map that identifies boundaries of land ownership. These maps are available for public use, but are maintained by the government. Information found on this type of map may include: who owns the land, zoning, tax rates, and certain items found on the property. The picture above shows an example cadastral map of what looks like to be a neighborhood. The separation of lots and their individual size is easily identifiable.
http://www.fig.net/cadastraltemplate/fielddata/d2.htm
Monday, November 7, 2011
Line Graph
A line graph is a type of geovisualization. The graph is used to compare an independent variable verses a dependent variable. The dependent variable is usually time. Line graphs can consist of one or more lines. Data from an experiment is plotted on the graph, and a line is used to connect the data to show a trend. A line graph is an extension of a scatter plot and has many similar characteristics. The picture above shows a line graph of the amount of people who switch from AT&T to MCI over a period of time. The trend shows a positive correlation between time and number of people who switched companies.
http://mste.illinois.edu/courses/ci330ms/youtsey/lineinfo.html
Pie Chart
A part chart is a type of geovisualization. It is a chart that is used to compare different dependent variables from a common independent variable. The graph is in a circular pie shape and is usually multiple colors to help for easy analysis. Pie charts can be used to measure many things including both quantitative and qualitative data. The pie chart above shows the results of the question: what is your favorite movie? The chart shows how many students were asked and how many chose each different category. The percentages were also calculated.
http://www.mathsisfun.com/data/pie-charts.html
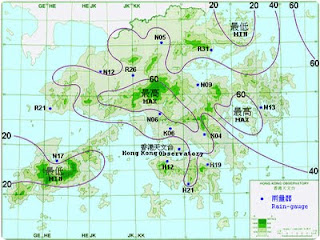
Isohyet
An isohyet is a type of contour map that measures the equal amount of rainfall in a given area during a certain time period. Due to the fact that the amount of rainfall can vary from year to year, theses maps can help analyze climate variability. The picture above is an isohyet from Asia. Areas that received the same amount of rainfall are connected by contour lines. According to the map, most of the area received 40 (can’t tell units) of rain.
http://www.einfopedia.com/tag/what-is-isohyet
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)